HOWTO-Tunneling through PuTTY
Linux Users
- Right click on the desktop and select Open Terminal
- Type ssh username@gluey.phys.uconn.edu
- After entering your password this will put you in your home directory (/home/username)
Mac Users
- Open Finder and navigate to Applications->Utilities and double-click on Terminal OR click on the magnifying glass in the top right corner and search for Terminal
- Type ssh username@gluey.phys.uconn.edu
- After entering your password this will put you in your home directory (/home/username)
Windows Users
The recommended program to use is PuTTY. Download the putty.exe file at the link provided. The following guide will assume you are using PuTTY.
- Open PuTTY
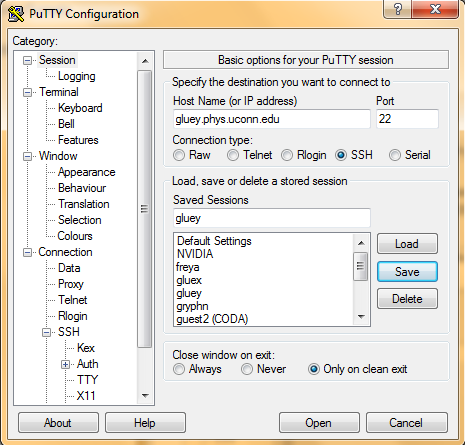
- On the main screen, under Host Name (or IP address), type gluey.phys.uconn.edu
- In the Saved Sessions box type gluey and click the save button
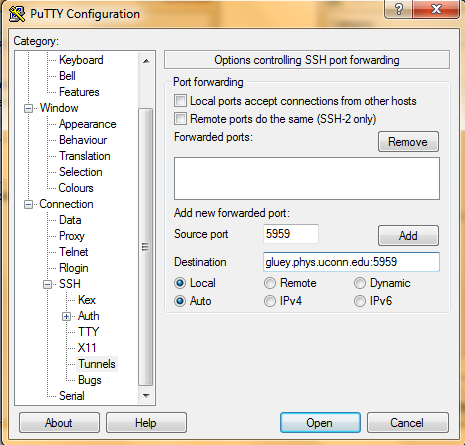
- In the left tree structure go to Connection->SSH->Tunnels. This grants the local source port the ability to see through a "tunnel" to the remote port. If a VNC session is desired then the port number here needs to match the port number of the VNC session. In this example a VNC session would need to be port 60. Only add 1 tunnel. Choose your own port number.
- In Source Port type 5960
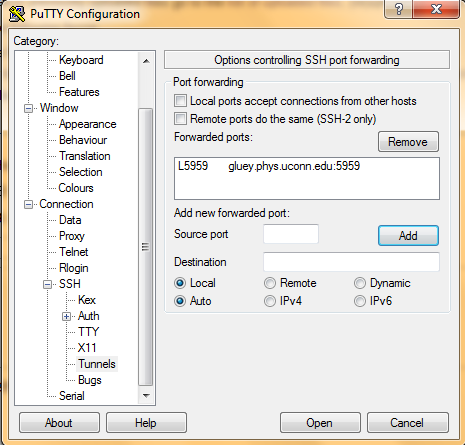
- In Destination type gluey.phys.uconn.edu:5960 and click the Add button
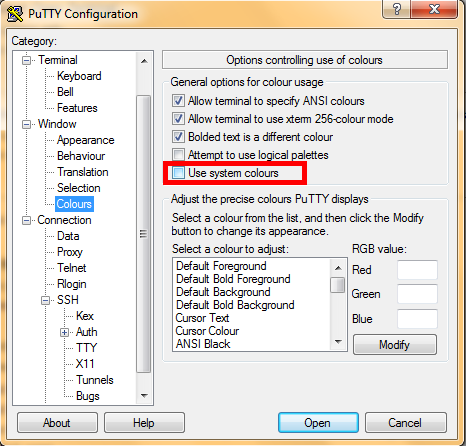
- In the tree structure go to Window->Colours
- If you would like your terminal to be black with white text leave the box Use system colours unchecked
- If you would like your terminal to be white with black text check the box Use system colours
- Return to the main screen (at the top of the tree structure click Session) and click the save button again
- With gluey loaded you can now click open
- The first time you connect a window should pop up. Click yes to connect, then login with your provided username and password
- After entering your password this will put you in your home directory (/home/username)
- After the initial setup, logging in requires you to open PuTTY and opening your saved gluey session