Active Collimator Installation Pictures
Active Collimator
The active collimator has been delivered to JLab by John Bartolotta. As of July 1, 2014 Alex Barnes is in charge of the assembly, testing, installation and analysis of the active collimator and the data collected with it.
- Alex's logbook can be viewed here.
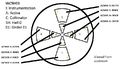
The active collimator is a beam position monitor that consists of a set of machined tungsten wedges placed in two concentric rings about a central hole of 5mm. When the beam hits a wedge it creates a current which can be readout through a preamplifier. Each ring consists of 4 wedges corresponding to +X, +Y, -X, and -Y directions.
Assembly
Components
- Screws
- brass
- round-headed
- 4-40 type
- 3/4 inch long
- Nuts
- brass
- 4-40 type
- 1/4 inch
- Drill bit used to drill out screw head
- 1/32 inch drill bit
- ream out the hole after using the drill bit to give it a taper
- the process is trial and error; drill and mount the RF connector until satisfied
- test connection by measuring the resistance from the RF signal connector to the screw
Pictures
Below are pictures of the assembling process
Installation
The active collimator has been installed in the collimator cave in Hall D. A shielding box was constructed out of plexi and placed above the active collimator.
Initial noise measurements
Initial noise measurements were recorded by Trent Allison on October 6, 2014. Below is a gallery of the waveforms from each wedge at each gain.
Monitoring screens
Acronyms
- EPICS - Experimental Physics and Industrial Control System
- IOC - Input Output Controller (software component)
- CSS - Control System Studio (application development environment)
- OPI file - Operator Interface file (application within CSS)
- AC - Active collimator
- Monticello - the MEDM main display gui that pops up when medm is started
- MEDM - Motif-based Editor and Display Manager (see here) used for graphical displays of active EPICS components by the accelerator, and accessed from the counting house by shift workers.
Viewing AC waveforms in Monticello
- Connect to a gluon machine in the Hall D counting house
- In the terminal window type the command monticello
- In the Monticello screen, move the mouse to the BPM menu item and click the left-most button to reveal a pop-up menu. Select Hall D Active Collimator Diagnostics from the bottom of the popup menu. This will pop up a new window with the active collimator information.
- Make sure the following are selected
- iochdcol
- SEE Norm Ops
- FastSee Light On
- Update Mode Continuous
- To change the sampling rate go to the lower left corner of the GUI where it says “samples to avg (500kHz)” and change it to 64. This takes 500kHz and divides it by 64.
- Go to Raw Wire Data Graph button near the bottom and you can open the plots for the inner and outer plates. If the option ends in ‘I’ then it refers to the inner wedges, if it ends with ‘O’ it refers to the outer wedges.
- Within this new window you can change the axes ranges by right clicking on an axis. This will pop up a new window that has options for the min and max for each axis.
Accessing CSS AC GUI
Analysis
Analysis software can be found on the hdops account on the gluon machines in the directory ~/acanalyzer.
The beam position is determined using a difference over the sum of different wedges.