Difference between revisions of "Mapping diamond surfaces using interference"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Using Maxwell's equations we can find solutions for a travelling wave comprised of two perpindicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields, whose direction can be giving by the Poynting vector. | Using Maxwell's equations we can find solutions for a travelling wave comprised of two perpindicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields, whose direction can be giving by the Poynting vector. | ||
[image of EM wave here] | [image of EM wave here] | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:emwave.jpg]] |
Revision as of 21:20, 28 February 2007
This page represents a ongoing project dealing with using interference patterns to map the surface of a diamond wafer. Since this is my first page, you'll have to excuse any blatant errors that I do not pick up on immediately. Currently this page will represent my work with Dr. Richard Jones on an approximation to the beam splitter featured in the Michelson interferometer. I will start by giving a brief introduction to electromagnetic radiation, then move on to the approximation itself (including graphs,etc.).
A Bit on Electromagnetic Radiation
Using Maxwell's equations we can find solutions for a travelling wave comprised of two perpindicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields, whose direction can be giving by the Poynting vector.
[image of EM wave here]
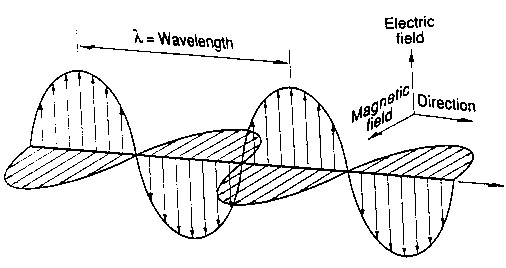
But, what if I need to make formulas? I have no idea what that will look like, but let's try it. We can also do vector equations, such as Gauss's Law
| (1) |
Next let's make some chapter headings.

